Medical facilities in ambulances are a critical component of modern emergency healthcare systems. These facilities are designed to provide immediate medical care and support to patients while they are being transported to a hospital or healthcare facility. The presence of medical facilities in ambulances can make a significant difference in the outcomes of medical emergencies, especially in cases of trauma, cardiac events, and other life-threatening conditions.
Here are some key aspects of medical facilities in ambulances:
Emergency Medical Personnel: Ambulances are typically staffed with trained medical personnel, such as Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs) or paramedics. These professionals are skilled in providing various levels of medical care, from basic first aid to advanced life support measures.
Medical Equipment: Ambulances are equipped with a wide range of medical equipment and supplies to assess and stabilize patients. This includes items such as defibrillators, oxygen tanks, intravenous (IV) lines, medications, airway management tools, and monitoring devices like ECG machines and pulse oximeters.
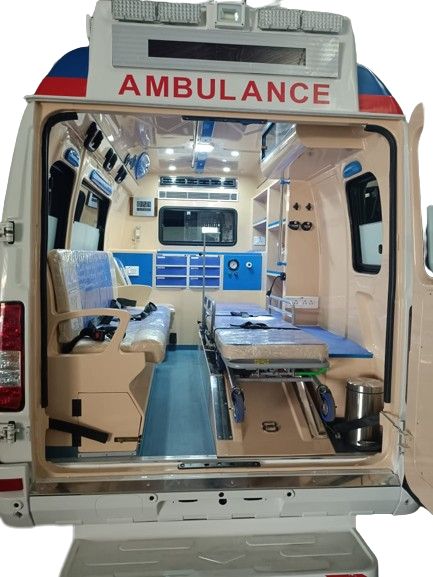
Advanced Life Support (ALS) and Basic Life Support (BLS): Ambulances may be classified as ALS or BLS units. ALS units are equipped to provide advanced medical interventions, such as administering medications, performing intubations, and delivering electrical shocks in cases of cardiac arrest. BLS units primarily offer basic care like wound dressings, splinting fractures, and CPR.

Mobile Intensive Care Units (MICU): In some regions, ambulances are designated as MICUs, which means they are staffed with highly trained paramedics and equipped with advanced medical equipment, making them capable of providing intensive care during transport.
Communication Systems: Ambulances are equipped with communication systems that enable paramedics to maintain contact with the hospital’s emergency department. This allows for the transmission of vital patient information and receiving medical guidance from doctors en route.
Specialized Ambulances: Some ambulances are designed for specific purposes, such as neonatal transport units for premature infants, stroke units with telemedicine capabilities, or bariatric units equipped to safely transport obese patients.
Infection Control Measures: In recent years, the importance of infection control in ambulances has been highlighted, especially during pandemics like COVID-19. Ambulances are equipped with infection control measures, including personal protective equipment (PPE) for medical staff and measures to decontaminate the vehicle after transporting infectious patients.
Accessibility: Ambulances are designed to be accessible to patients with varying levels of mobility. They often have hydraulic stretchers or ramps to safely load and unload patients, including those with limited mobility or spinal injuries.
Documentation and Reporting: Ambulance crews are responsible for documenting the patient’s condition, vital signs, medications administered, and the care provided during transport. This documentation is crucial for continuity of care when the patient arrives at the hospital.
In conclusion, medical facilities in ambulances play a pivotal role in providing timely and effective care to individuals in medical emergencies. These facilities, along with skilled medical personnel, ensure that patients receive appropriate care from the moment they are encountered by emergency services until they reach the hospital. This integrated approach to pre-hospital care significantly improves the chances of a positive outcome for patients in critical situations.

